Using an Impact Analysis
Kosow and Gaßner identified a group of scenario techniques which they called systematic-formalized. These techniques begin with the identification of key factors, and then build scenarios based on the different combinations of these factors.
One of the techniques is the Impact Analysis. In this technique, identified key factors are arranged in a grid, with a row and a column for each factor. Each factor is then rated based on the impact that that factor might have on each of the factors across the columns.
Impact is rated on a scale, either from 0 through 3, where:
- 0: No influence
- 1: Weak relationship
- 2: Medium relationship
- 3: Strong relationship
or to provide more variability, from 0 through 5:
- 0: No influence
- 1: Very weak influence
- 2: Weak influence
- 3: Moderate influence
- 4: Strong influence
- 5: Very strong influence
This example from Kosow and Gaßner shows how this is laid out and scored:
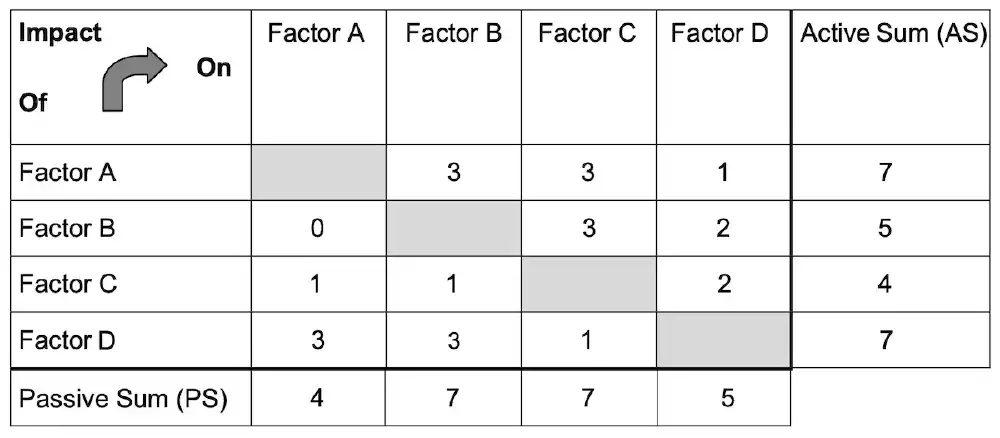
Once all of the influences have been scored, the values in each row are summed to get the Active Sum for that factor, and each column is summed to get the Passive Sum for that factor.
The example uses a range of 0 through 3 for scoring, so using Factor B as an example:
Sum the columns in Factor B row to get Active Sum
- Factor B has No influence on Factor A
- Factor B has a Strong influence on Factor C
- Factor B has a Medium influcen on Factor D
This gives Factor B an Active Sum of 5 (0 + 3 + 2).
Sum the rows in Factor B column to get Passive Sum
- Factor A has a Strong influence on Factor B
- Factor C has a Weak influence on Factor B
- Factor D has a Strong influence on Factor B
This gives Factor B a Passive Sum of 7 (3 + 1 + 3).
The Active Sum is an indication of how strongly that factor influences others, while the Passive Sum is an indicator of how strongly that factor is influenced.
Based on their relative Active and Passive sums, the factors can then be categorised into 4 typologies:
- Active factors have a high active sum and a low passive sum. These factors are responsible for driving change. Kosow and Gaßner described these factor as levers.
- Passive factors (also known as reactive) have a high passive sum and a low active sum. Because these factors are highly influenced, they are useful indicators within a system.
- Critical (or dynamic) factors have a high active sum and a high passive sum. These factors exert a large amount of influence but are themselves also subject to influence. These factors have a high sensitivity to change and are typically important operational factors within a system. Critical factors should not be considered in isolation from the system in which they function.
- Buffering (or lazy) factors have both a low active and a low passive sum. These factors have the capacity to absorb change and provide a buffer against both sudden change but also against a lack of change.
The relative values of what constitute high and low will depend on the scoring for your specific example.
Putting it into practice
I’ve been through many variations of creating these impact analysis matrices, using paper, Powerpoint slides, Google sheets and eventually Miro.
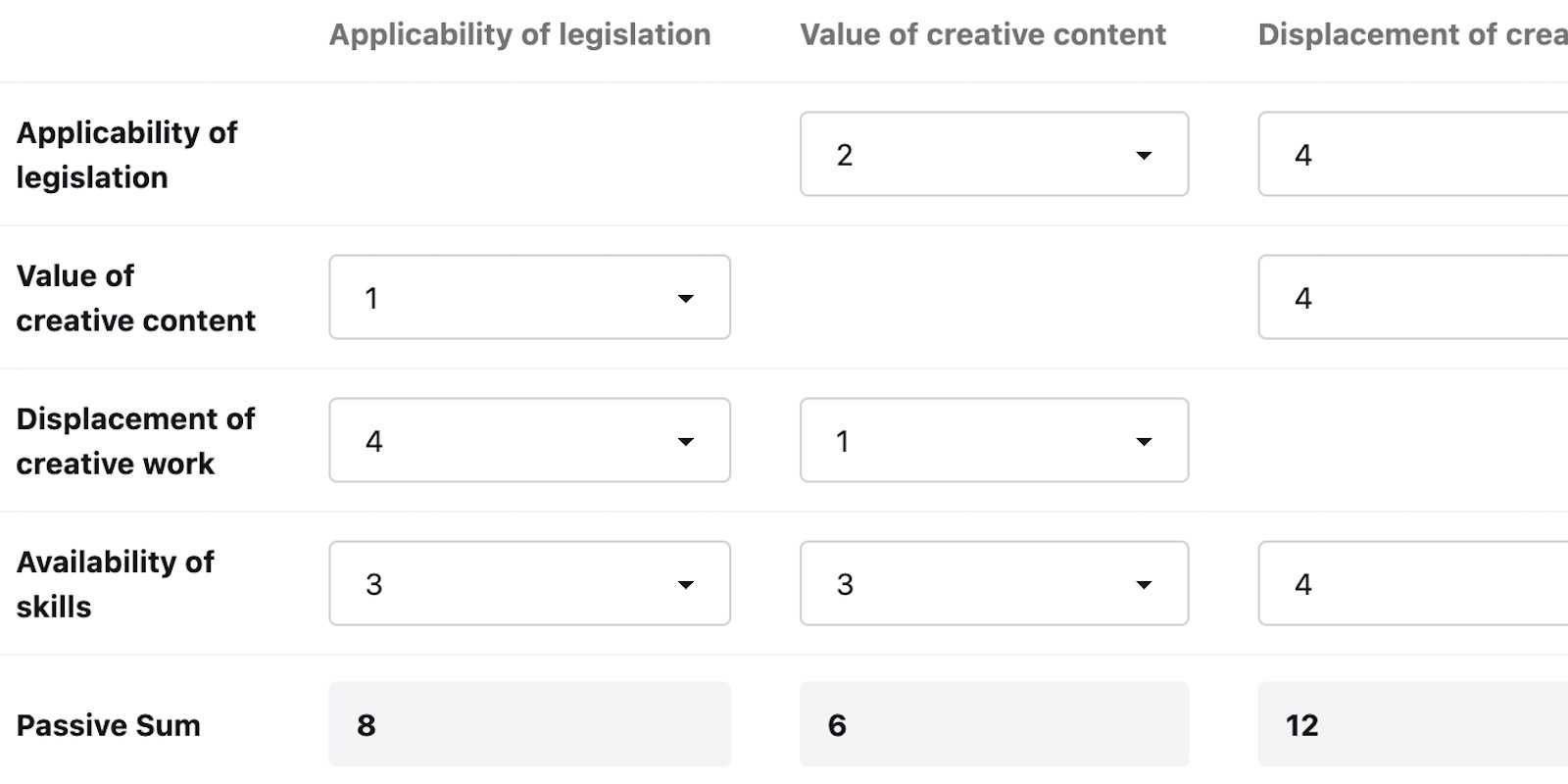
This is the version I created for my MPhil Futures Studies:
All of these techniques are fairly manual, so I’ve built an online version that tries to take some of the tedium out of the process: https://foresight.allankent.com/impact_analysis/.
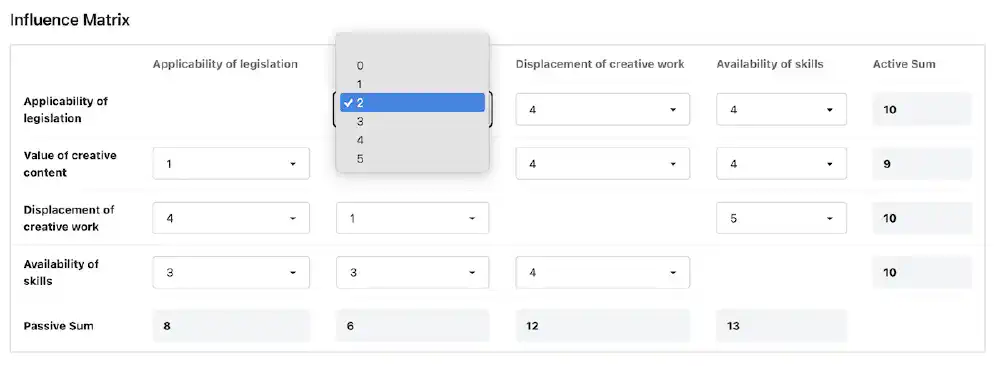
When opening the page you are presented with a config panel. Add each of your key factors on a new line and select the scoring range. It defaults to 3 as the max influence score, but you can increase that to 5.

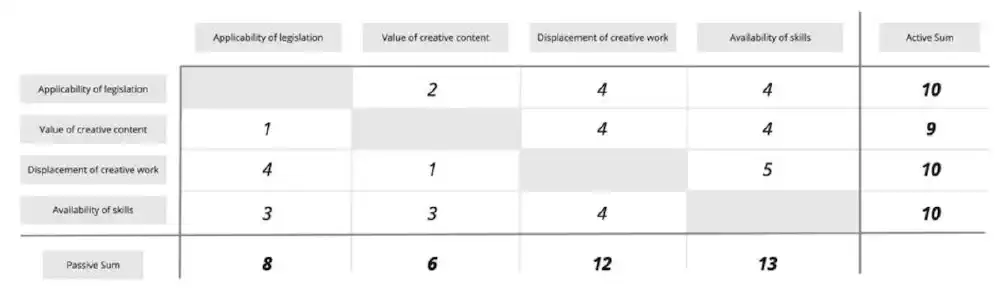
This dynamically creates the matrix, with options to select the influence score at the intersection of each of the factors. As you score each one, the Active and Passive sums will automatically update.
A table at the bottom of the page is also automatically updated to show the Active and Passive sums for each Factor individually.

References
Kosow, H., & Gaßner, R. (2007). Methods of future and scenario analysis: Overview, assessment, and selection criteria. Dt. Inst. für Entwicklungspolitik.